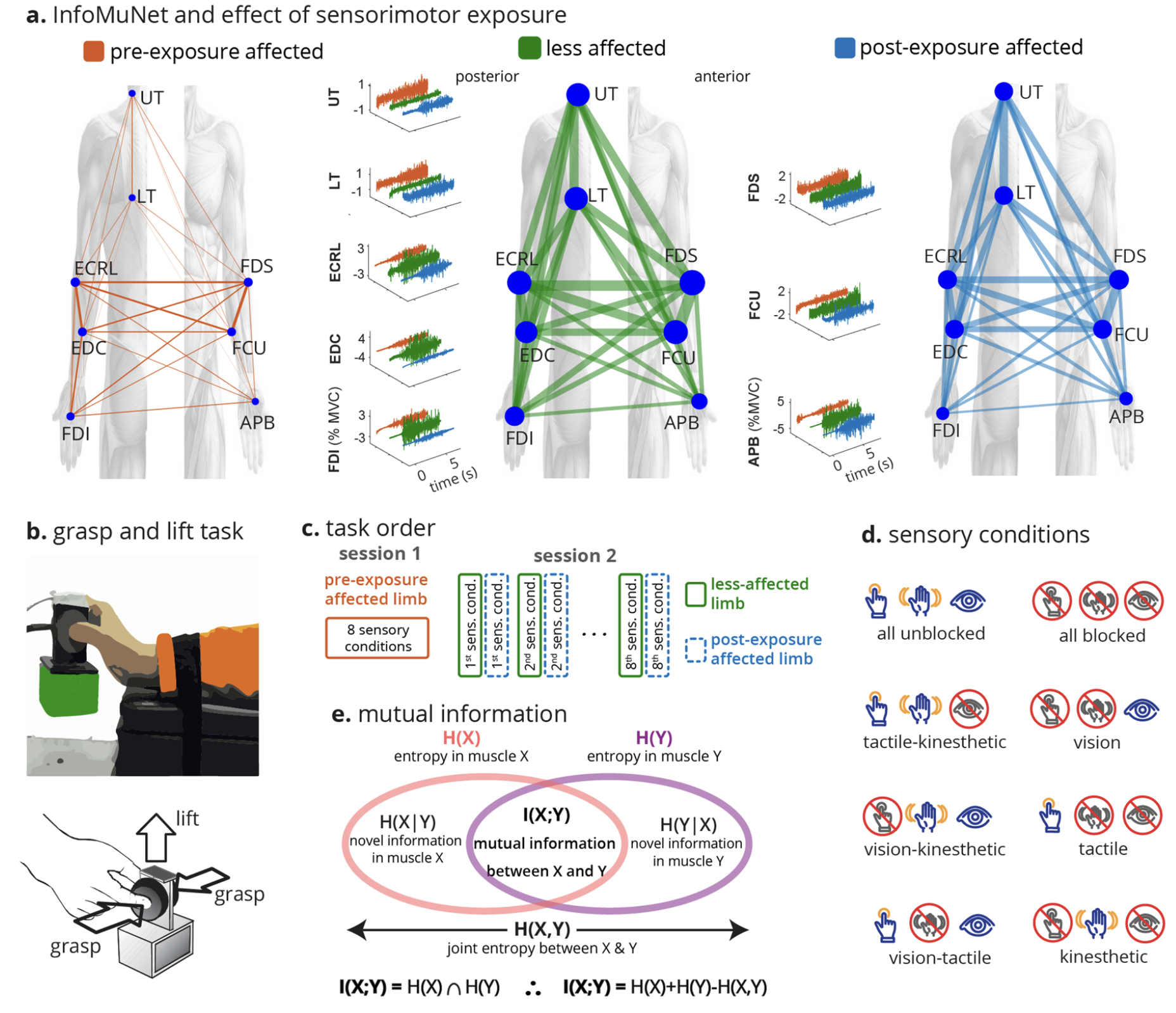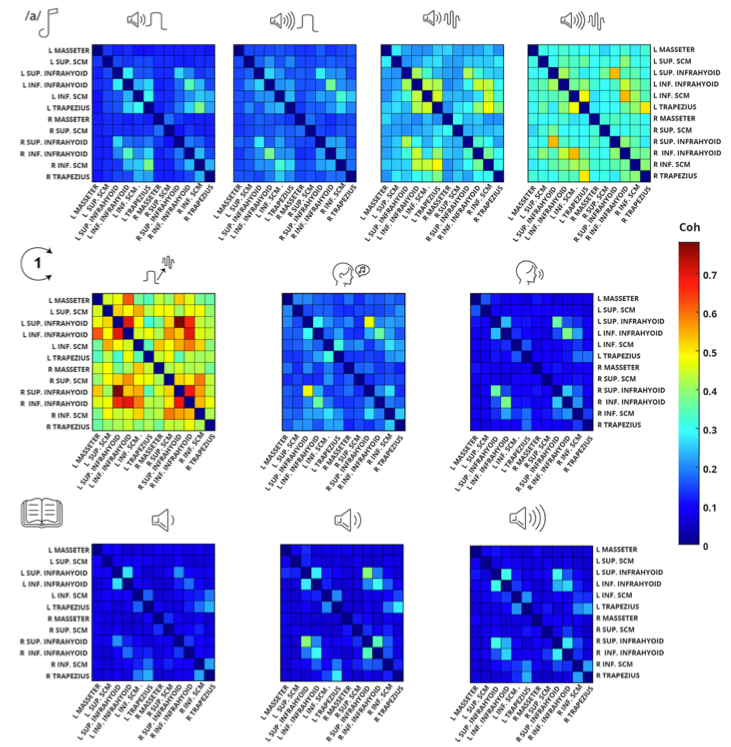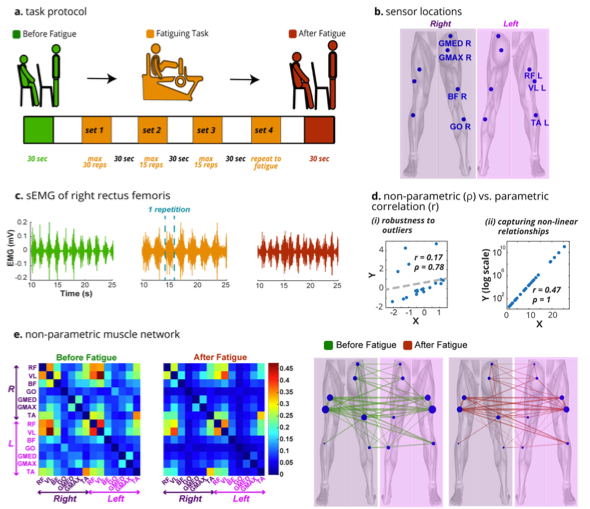
Non-Parametric Functional Muscle Network as a Robust Biomarker of Fatigue
We show that the effects of fatigue on muscle coordination and neural drive can be reliably characterized using a non-parametric functional muscle network. The network demonstrated a consistent decrease in connectivity after the fatigue intervention, as indicated by network degree, weighted clustering coefficient (WCC), and global efficiency. The graph metrics displayed consistent and significant decreases at the group level, individual subject level, and individual muscle level. The proposed approach has the potential to be a sensitive biomarker of fatigue with superior performance to conventional spectrotemporal measures.