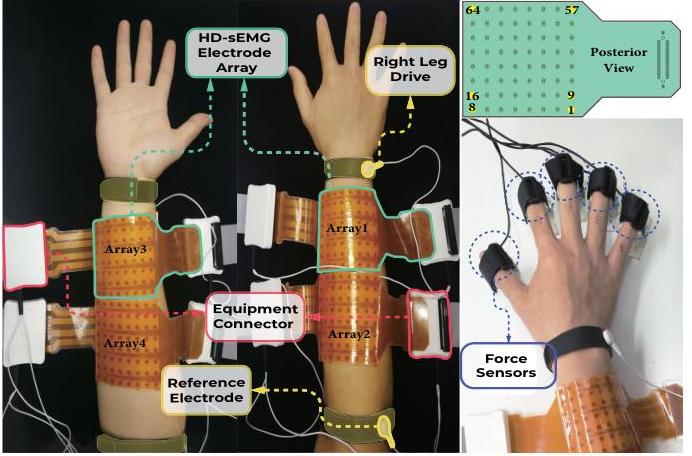
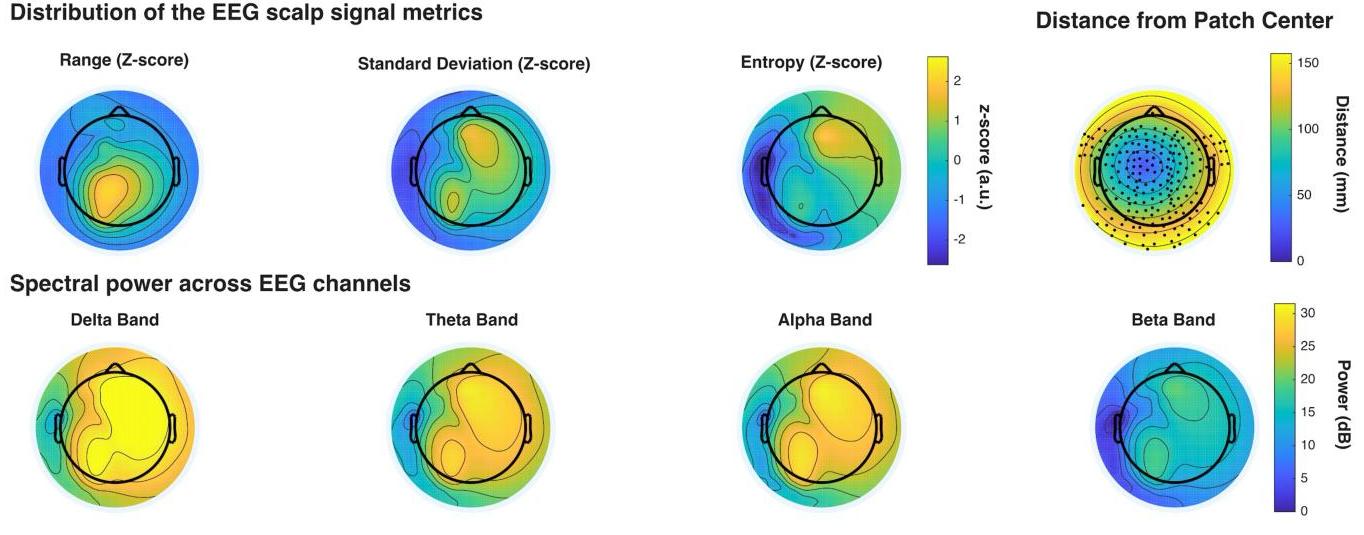
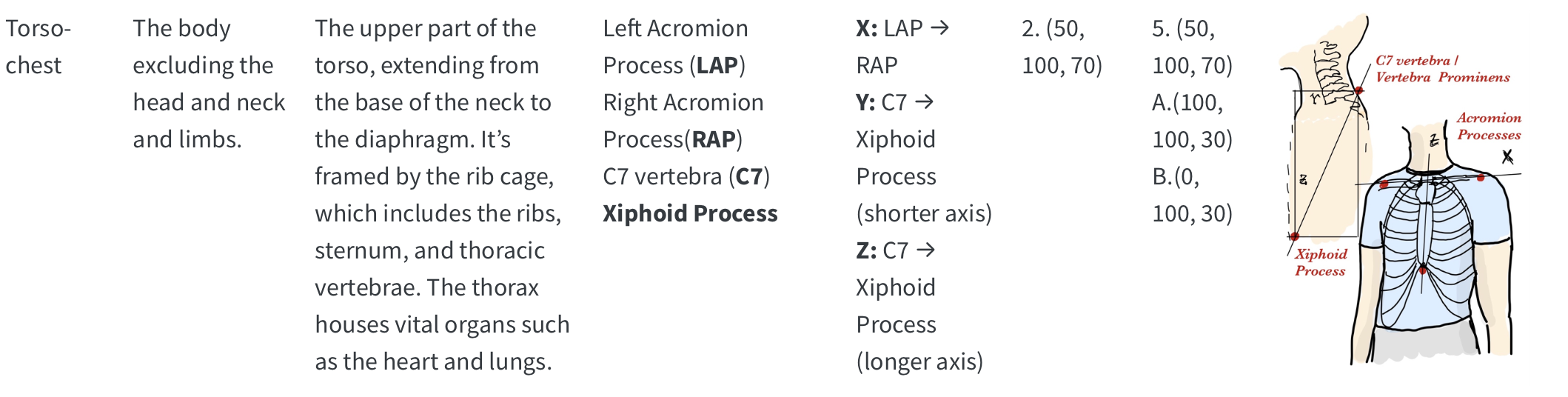
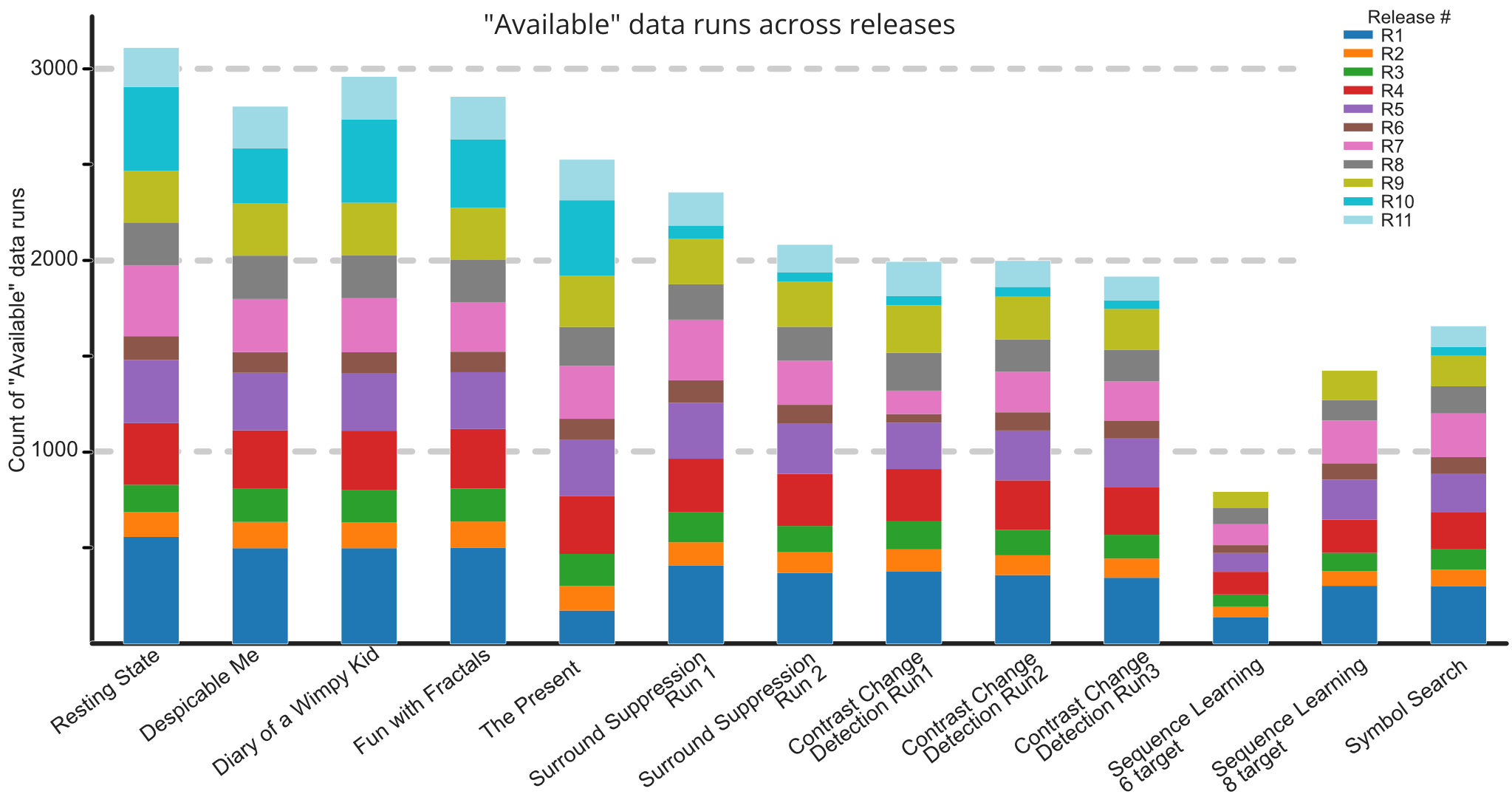
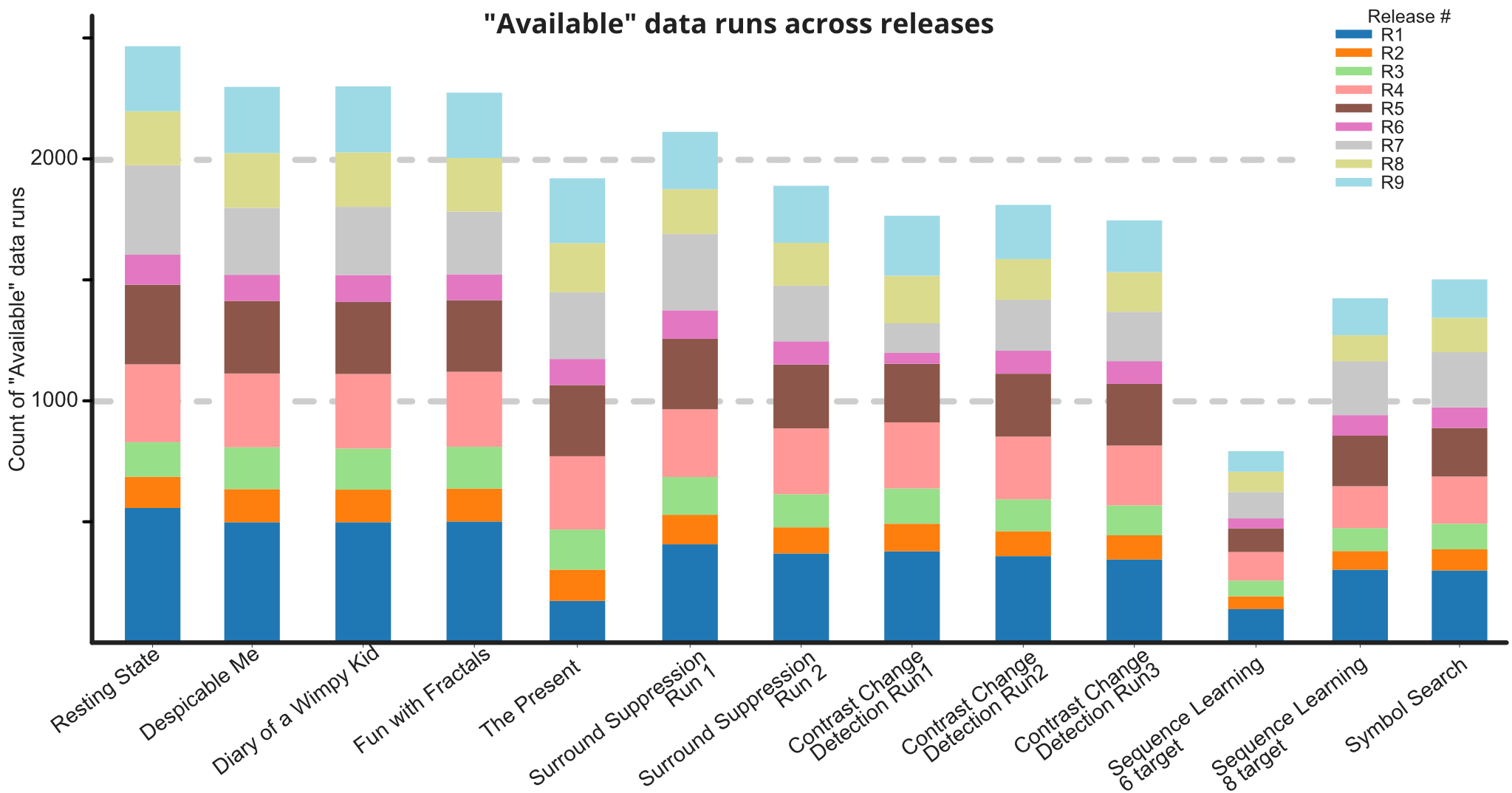
The HBN-EEG dataset provides a comprehensive collection of high-density EEG recordings from the Healthy Brain Network project, formatted in the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) standard. This dataset includes annotated behavioral and task-condition events, making it ready for various types of analysis without the need for extensive preprocessing. With data from over 2,600 participants, the HBN-EEG dataset supports the development and validation of EEG analysis methods, including machine learning and deep learning approaches. Additionally, it aims to facilitate the creation of EEG-based biomarkers for psychiatric disorders, offering valuable insights into brain function and mental health.