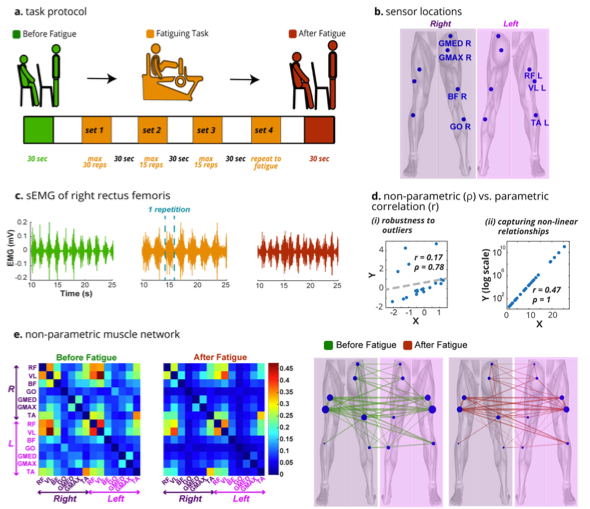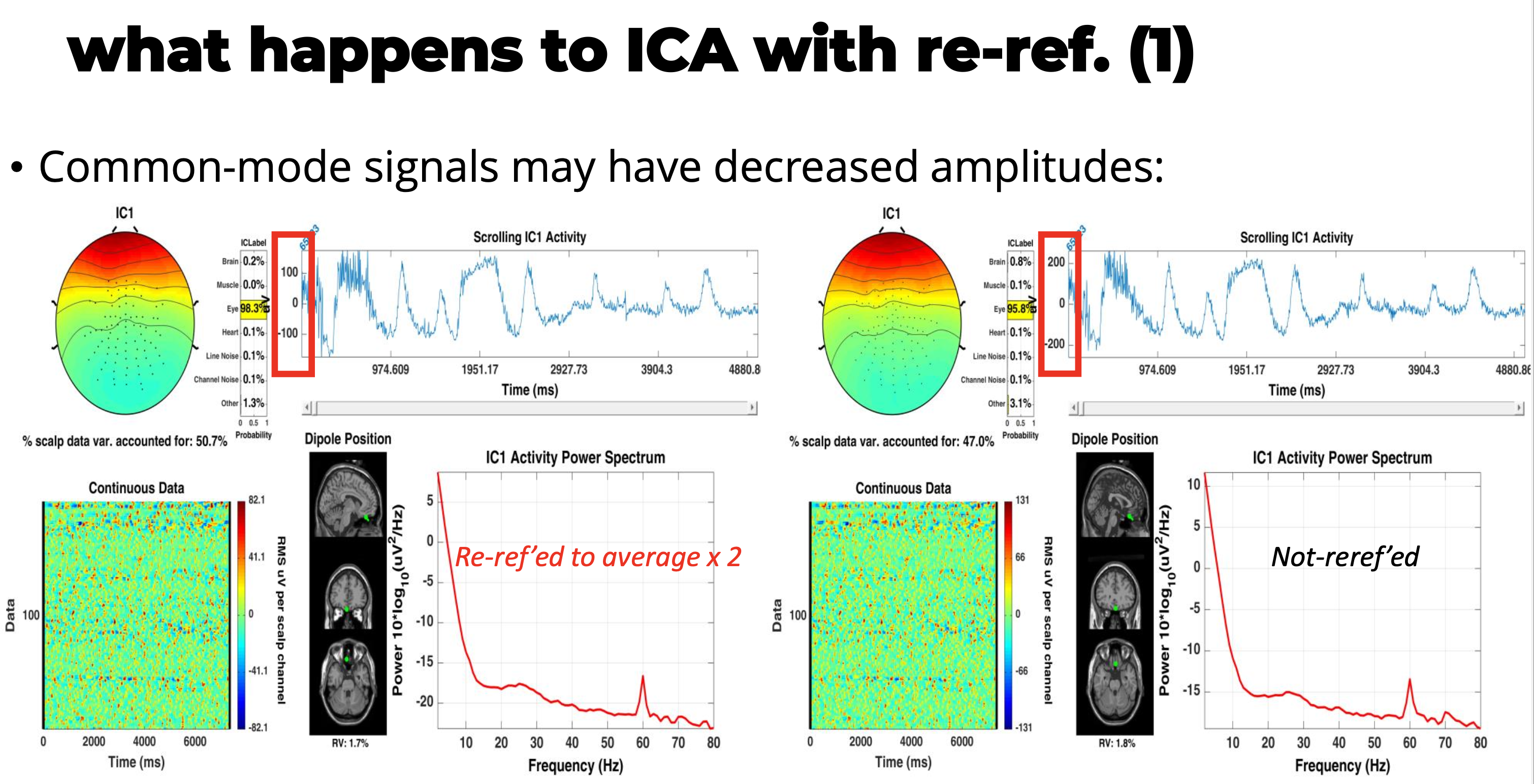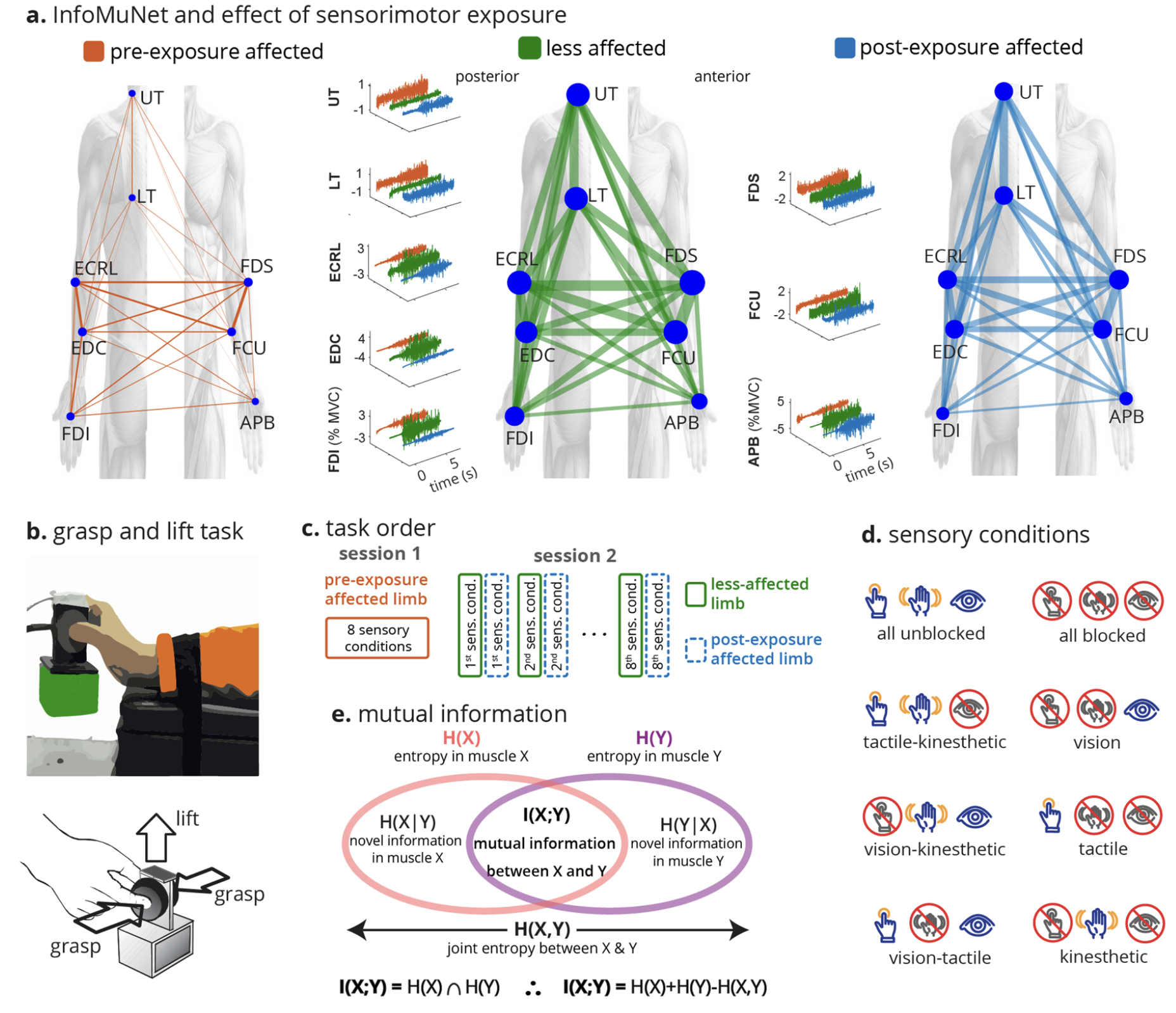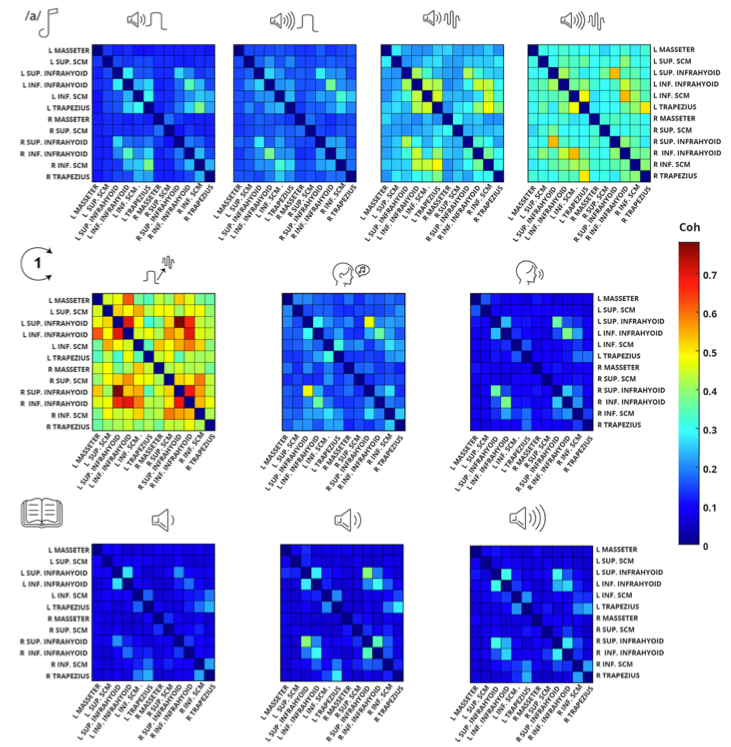
System and methods for biosignal detection and active noise cancellation
We developed a novel EEG system with a dual-electrode net structure for noise reduction and precise biosignal capture. Incorporating advanced software for signal processing, this invention enhances EEG accuracy, reduces setup complexity, and broadens EEG applications, including brain-computer interfaces, through real-time noise separation and immersive noise layering techniques.