The Lab Streaming Layer for Synchronized Multimodal Recording
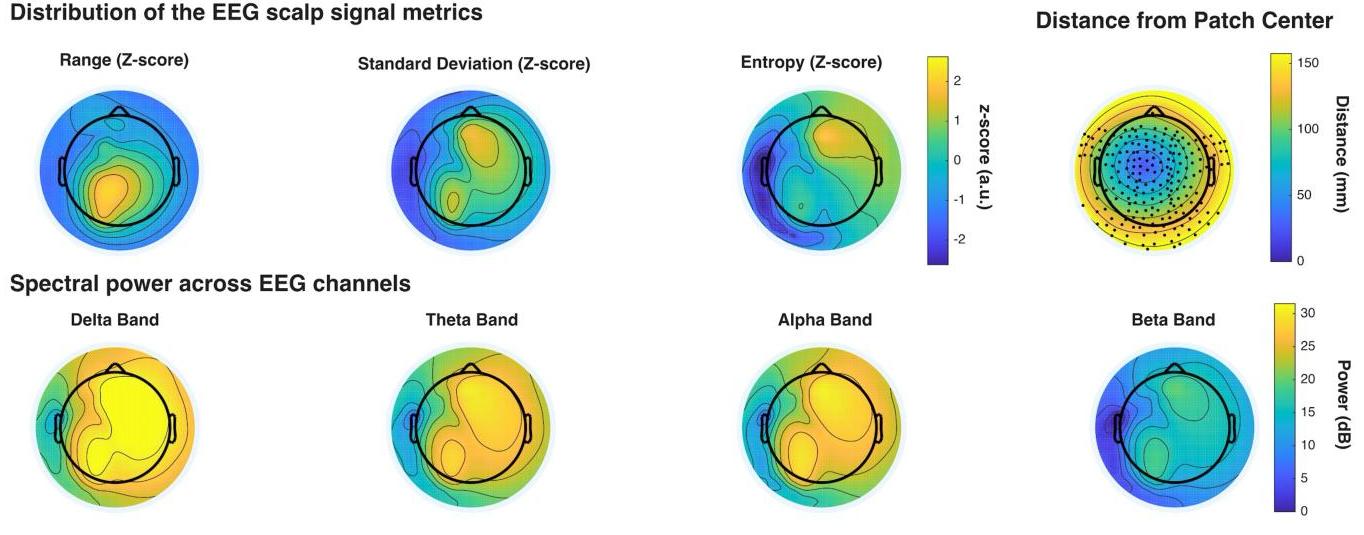
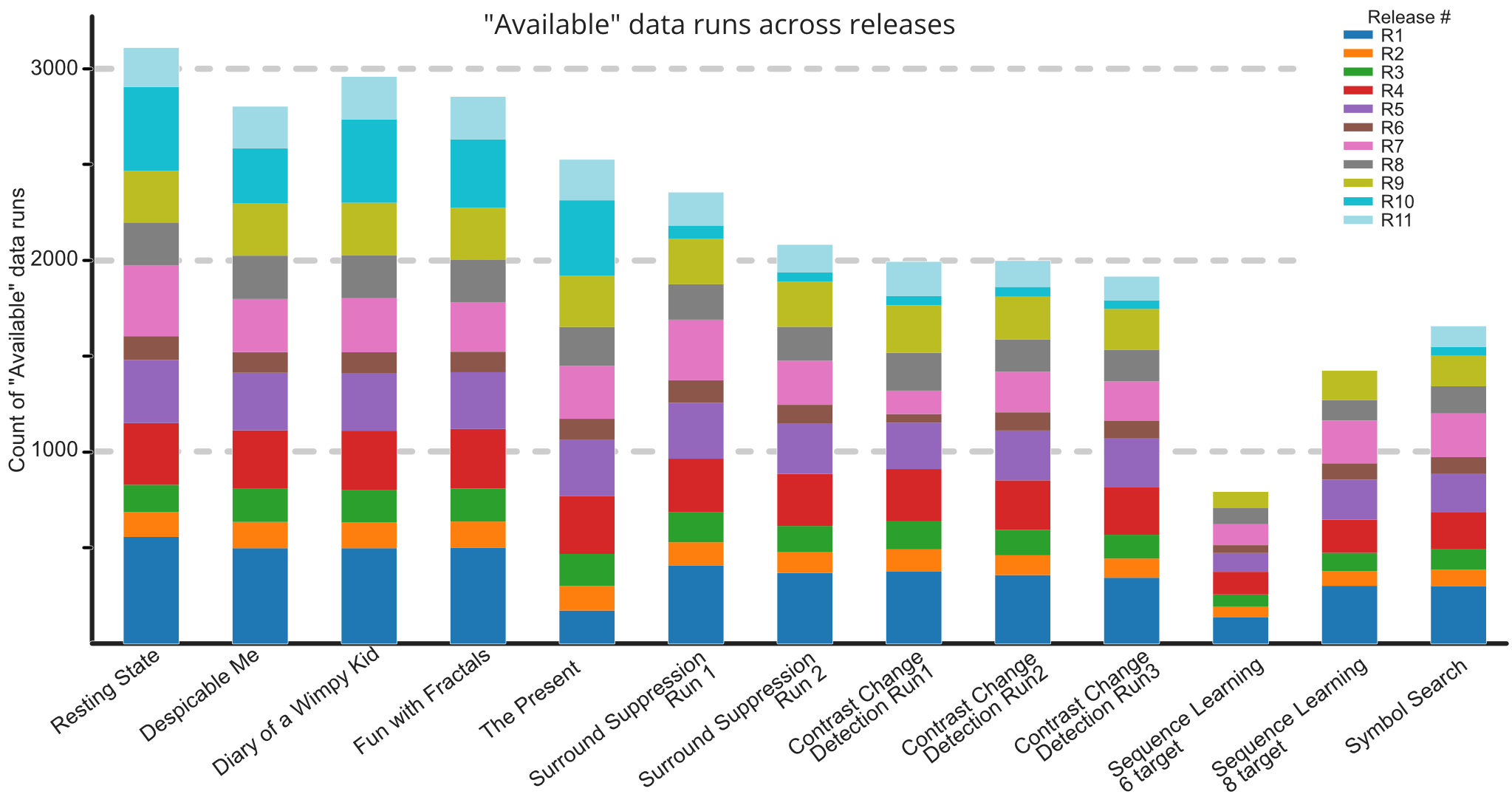
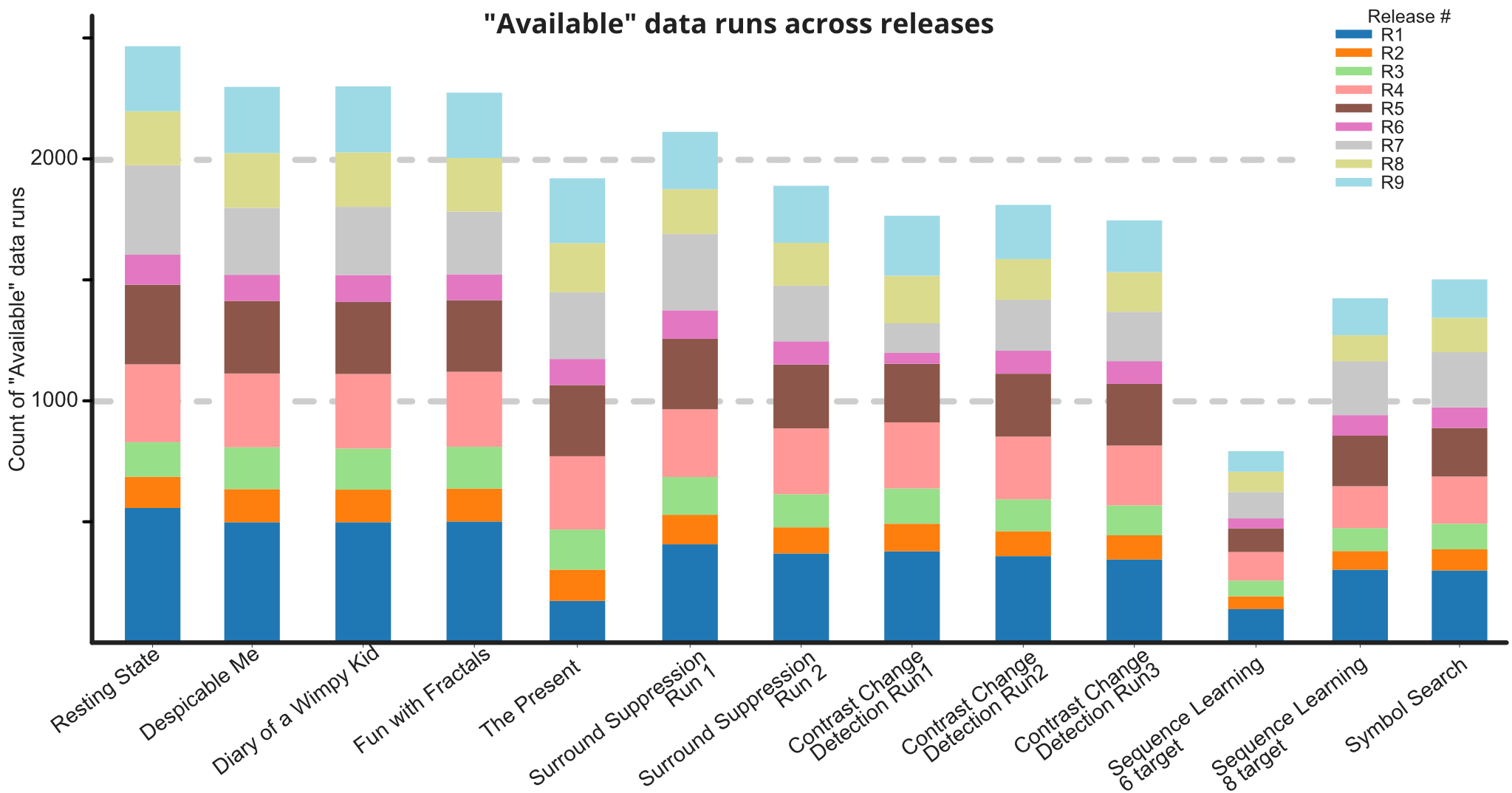
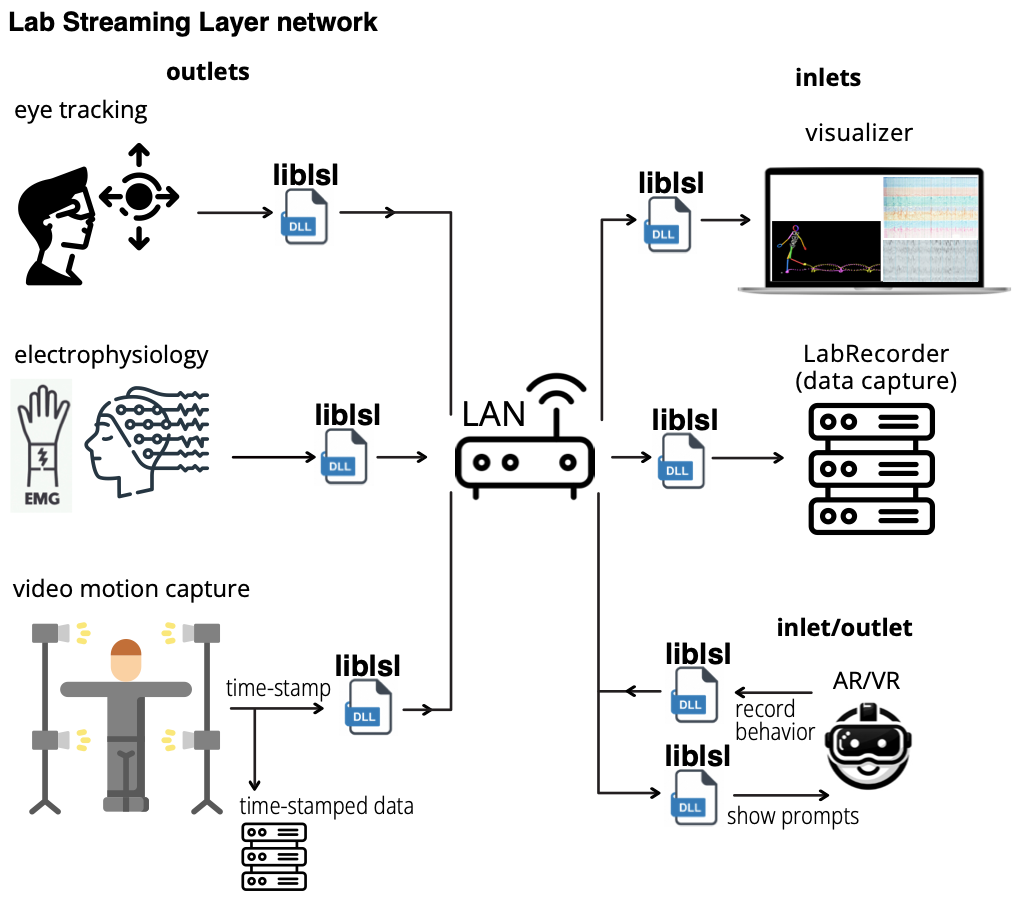
The Lab Streaming Layer (LSL) presents a software-based solution for synchronizing data streams across multiple instruments in neurophysiological research. Utilizing per-sample time stamps and LAN-based time synchronization, LSL ensures accurate, continuous recording despite varying device clocks. It automatically corrects for network delays and jitters, maintaining data integrity through disruptions. Supporting over 150 device classes and compatible with numerous programming languages, LSL has become a vital tool for integrating diverse data acquisition systems. Its robustness and adaptability have extended its application beyond research, into art, performance, and commercial realms, making it a cornerstone for multimodal data collection and synchronization.